
How Do Large Language Models (LLMs) Work?
Continuing the topics related to Artificial Intelligence, we will now talk about Large Language Models or LLMs (Large Language Models).
An LLM is created with a very large amount of data and words (billions), so it can predict what the user wants to say and complete sentences, as well as learn in an evolutionary way.
These models are trained with large volumes of data from the internet and learn patterns of how words and phrases are commonly used together. When a new text input is provided, an LLM will try to predict or generate the most likely continuation of that text based on what it learned during training. These models are trained with large amounts of text data to learn patterns and relationships between entities in the language.
They can understand complex textual data, identify entities and relationships between them, and generate new text that is coherent and grammatically accurate.
Although the mathematical principles behind these LLMs may be complex systems, a basic understanding of the architecture used to implement them can help you better grasp the concepts of how they work.
Large-scale models are based on transformer architecture, which builds upon and expands on some techniques that have proven successful in modeling vocabularies to support NLP tasks and, particularly, language generation.
Transformer models are trained with large volumes of text, allowing them to represent semantic relationships between words and use these relationships to determine likely sequences of text that make sense.
- An encoder block that creates semantic representations of the training vocabulary.
- A decoder block that generates new language sequences.
In practice, specific implementations of the architecture vary: for example, the BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers) model developed by Google for the search engine support only uses encoder blocks, whereas the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) model developed by OpenAI uses only the decoder block.
Next, we present some of the most relevant large language models today. These models perform natural language processing and influence the architecture of future models.
According to the ranking of Chatbot Arena as of today, these are the TOP LLMs:
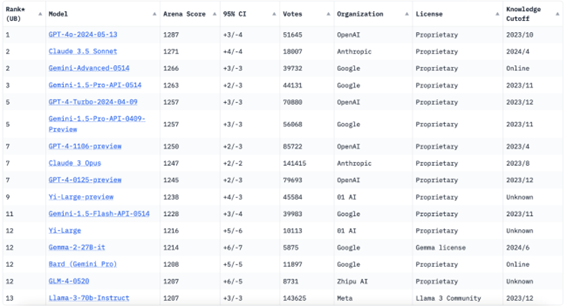
Focuses on constitutional AI, which shapes the outcomes of AI guided by a set of principles that help the AI assistant to be helpful, harmless, and precise. Claude was created by the company Anthropic.
A "generative" model designed to predict the next word in a sequence of text based on the previous sequence. GPT uses a unidirectional approach for training, processing text from left to right or sequentially and learning to generate text based on what it has seen before.
Designed as a "comprehension" model of language, BERT processes text bidirectionally, meaning it learns the context of a word based on all the other words in a sentence. It uses a technique called MLM or Masked Language Model, where some words from the input are hidden or masked. In this environment, the model tries to predict these words based on the context provided by the non-hidden words.
Gemini models are multimodal, meaning they can handle images, audio, and video, in addition to text. Gemini is also integrated into many Google applications and products. The model replaced Palm in the chatbot feed, which was renamed Bard to Gemini after the model change.
It is a family of open-source language models from Google that were trained with the same resources as Gemini. The Gemma models can be run locally on a personal computer.
Large Language Model Meta AI (Llama) is the LLM from Meta released in 2023. Llama was initially launched for approved researchers and developers, but it is now open source.
Although LLMs are a recent phenomenon, their precursors date back decades. Find out how the recent precursor Seq2Seq and the distant precursor ELIZA set the stage for modern LLMs.
What is the future of LLMs?
The introduction of large language models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Llama, which can answer questions and generate text, points to interesting possibilities in the future. Slowly but surely, LLMs are achieving human-like performance. The immediate success of these LLMs shows great interest in robotic-type LLMs that emulate and, in some contexts, outperform the human brain. Below are some thoughts about the future of LLMs:
- Greater Capabilities
- Audiovisual Training
- Workplace Transformation
- Conversational A

Ricardo Oliveira
Head Tech & Innovation
Author
FAQ
LLMs are trained on massive amounts of text data to predict and generate meaningful sequences. They use transformer architecture, which helps them understand and generate text by learning semantic relationships.
BERT is bidirectional and designed for language comprehension, while GPT is unidirectional and generative, focused on predicting the next word in a sequence.
Popular LLMs include Claude (Anthropic), GPT (OpenAI), BERT (Google), Gemini (Google), and LLAMA (Meta), which are used for tasks like text generation, comprehension, and multimodal processing.
Dialogi AI
Find out how our solutions with empat. AI can revolutionize customer service in your business.
Recent Post
- All Posts
- Customer Experience
- Design and Communication
- Design e Comunicação
- Design y Comunicación
- Ethics and Society
- Ética e Sociedade
- Evolution and Impact of AI
- Experiencia del cliente
- Experiência do Cliente
- Sem categoria
Categories
Tags
Dialogi | AI | Human-Machine Interaction | Virtual Assistants | Automation | Future of Technology | Digital Communication




